Table of Contents
*This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
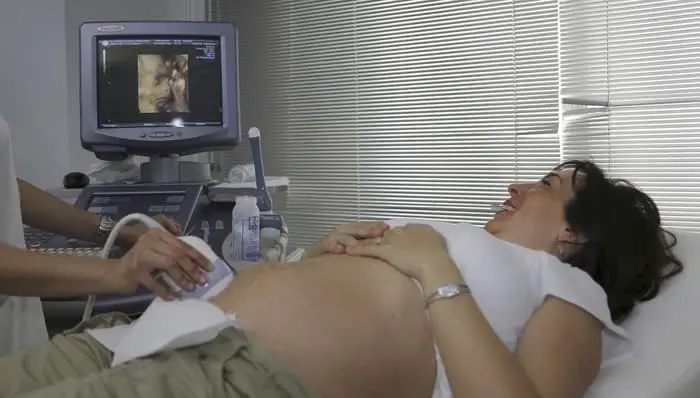 image source: Pixabay
image source: Pixabay
Expecting parents know the joy of seeing their baby for the first time through the use of ultrasound. Now, with 4D ultrasound, images of a new baby are clearer and more detailed than ever, and the benefits to both baby and mother abound.
What Is 4D Ultrasound?
The significance of 4D ultrasound is a technological benchmark as it brings the actual movements and expressions of a fetus into the present with real-time video reproduction from inside the womb. Sound waves create the image, taking the viewing experience to a whole new level. To understand the 4D ultrasound procedure think of the traditional 3D ultrasound which displays a three-dimensional image of the baby or body part being examined. The 4D ultrasound produces a visual effect nearly identical to viewing a real-time video. This technology makes it possible to see exactly what a baby is up to at that moment inside the womb.
Imagery is so precise that one can see the baby sucking its thumb, yawning, or smiling. There is a demand for ultrasound technicians who have the skill-set to conduct 4D ultrasound procedures. The Bureau of Labor Statistics expects an increase of 44% in diagnostic medical ultrasound by the year 2020.
Expectant mothers can view clearer, real-time images of their babies in the womb—but how does it work? The technician moves a transducer (a hand-held device that converts differences found within the body, such as pressure, into an electrical signal) along the abdomen. This movement sends sound waves through the abdomen and uterus. The sound waves bounce off the baby in the form of echoes and the monitor picks them up translating them onto the screen.
As the baby kicks and moves around, the patient and tech can view the images on the ultrasound screen, making it the most discussed form of ultrasound technology. However, the most valuable benefit of having a 4D ultrasound procedure is that it produces clearer, more discernable images which show more detail than results from 2D views. Hence, doctors have a real-time diagnostic tool at the patient’s bedside. The differences between 2D, 3D and 4D ultrasound are:
- 2D ultrasound sends and receives waves to create a flat, black-and-white image of the transverse and sagittal planes
- 3D ultrasound adds the coronal plane, providing a look at the outer contour and shape of the uterus
- 4D ultrasound system uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the body
Benefits Of Real-Time Video
Time is valuable and critically important when diagnosing medical conditions. The 4D ultrasound method produces instant results saving time for both the patient and doctor assuring maximum value for time spent. In gynecology, patients and their doctors seek to optimize their results which makes the 4D ultrasound the perfect choice.
The results are instantaneous, enabling patients to receive their diagnostic imaging test results right there in the office. There is no longer a need to make additional appointments, travel to various facilities or miss work for test results. And, if treatment is necessary, it won’t have to wait. Additional benefits include:
- Measuring the mucous membrane lining the uterus
- Identifying endometrial hyperplasia
- Tumor detection and evaluation
- Assessment of uterine growths and abnormalities
- Visual detection of pelvic abnormalities
- Aid in the origin of flank (kidney) pain
- Locate IUD placement
- Detection and measurement of cysts or polyps
- Increased confidence between doctor and patient
The Benefit of Patient Confidence
Sharing this ultrasound experience with your technician is intimate and personal. Patients get their information immediately, allowing them to point to the area in question without having a medical background. They can react and include the tech or doctor in decision-making during the procedure rather than having to view test results replete with numbered lists and language exclusive to the medical profession.
4D technology allows men undergoing the exam and pregnant women to see the same video as the doctor, opening the door to discussion, therapy and treatment options. Ultrasound technicians can immediately assess whether the patient understands a proposed treatment plan ensuring mutual agreement on what has transpired. Improved decision-making and understanding of their condition may also translate to better outcomes.
Detection Benefits in High-Risk Pregnancies
 image source: Pixabay
image source: Pixabay
3D and 4D ultrasound are more effective in detecting abnormalities in underdeveloped fetuses than 2D ultrasound. Using more advanced 4D ultrasound technologies often produces useful images when examining mothers with high-risk pregnancies. Some results reveal physical abnormalities in fetuses such as a cleft palate or club feet. 4D ultrasound is also effective in detecting behavioral problems and concerns affecting the brain and nervous system.
Additional Advantages in Using 4D Ultrasound
Ultrasound (also known as sonography or ultrasonography) is not exclusive to OB/GYN use. It is an essential medical imaging tool used in diagnosing medical conditions, screenings, and therapeutic treatments. New applications for 4D ultrasound uses are continually being discovered and fine tuned including:
- Determination of the baby’s due date
- Identifying placenta previa requiring delivery by C-section
- Assessment of the causes of leg swelling (deep vein thrombosis or a blood clot)
- Determining if the aortic valve (connected to the heart) needs replacement or repair
- Monitoring chronic liver disease (i.e. using ultrasound elastography)
- Diagnosing ectopic pregnancies where the embryo/fetus is developing outside the uterus
- Diagnosing congestive heart failure via echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart)
- Determination and prioritization of breast lesions (regarding those more likely to be malignant) reducing the need for unnecessary biopsies
- Detecting and locating abdominal aortic aneurysms
- Checking for testicular torsion by monitoring blood flow
- Monitoring nodules of the thyroid to determine the need for biopsy
Requirements for Technicians to Perform
The foundation of a successful 4D video starts with a clear 2D image. Failure to get a good 2D image will cause your video to be unreadable. Learning how to operate your machine correctly maximizes your chances of securing clear, readable results as it takes the initial step for you. Each ultrasound machine features settings that automatically find the most efficient settings for the ideal 2D image. The technician can locate the best settings in the application settings for the ultrasound’s probe.
Begin by finding the obstetric setting and locate the “2-3 trimester”, “mid-pregnancy” or similar setting for 20 or more weeks. Once selected you can scan the image. Your aim is to get the best 2D image of the baby’s profile which is usually accomplished by placing the ultrasound’s probe close to the pelvic bone either on the left or to the right side. Angle the probe’s head towards the cervix. You must reposition the probe from the other side if the spine comes into view.
How To Successfully Capture A Good 2D Image For 4D Ultrasound
Babies are rarely positioned perfectly, so it’s up to the technician to position the probe in a spot that produces a clear “baby-face” image. Successful 4D images contain the following characteristics:
- You will see the profile of the baby facing towards the probe producing a 4D picture of the baby’s ear
- When isolating the face, look for fluid in front of the baby’s face
- Make sure no obstructions block the baby’s face including hands, feet, umbilical cord, placenta, etc.
- Check for hands, arms, or feet in the image area
- Adjust the Gain (brightness control) as excessive brightness results in blurry images-too little results in dark images
4D Ultrasound Training
Persons interested in training to be 4D ultrasound technicians learn how to operate 3D/4D ultrasound machines on actual clients and a training phantom for determining the baby’s sex and how to perform 2D ultrasounds. Classes include:
- Probe orientation
- Fetal orientation
- Fetal heart rate
- Placenta placement
- Understanding of common abnormalities & how to handle them
- Basic and advanced 3D/4D HD scanning techniques
Conclusion
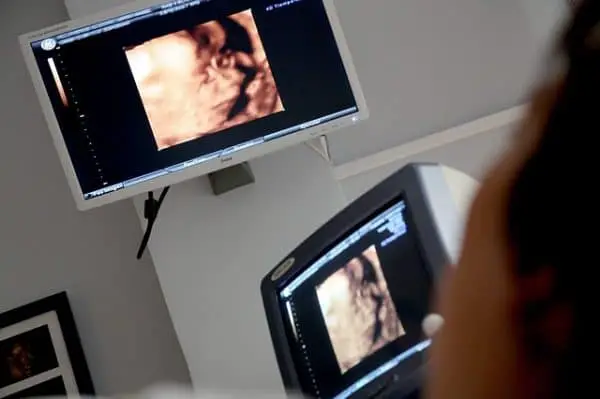 image source: Pixabay
image source: Pixabay
3D and 4D ultrasounds can display activities of the fetus that are not possible with 2D. Now we can observe the fetus while they’re yawning, blinking, smiling, moving their fingers, crying or even swallowing with 4D technology. This is critical information for some parents and patients, revealing minute details regarding fetal health and other medical conditions.
Doctors can observe and assess fetal activity just like a pediatrician would begin an exam of a newborn infant—except the exam takes place on screen. A keen eye can detect problems early on just by watching the fetus move, change positions and breathe. 4D ultrasound is also instrumental in promoting the bond between mother, father and child.
4D ultrasound is a diagnostic procedure requiring a doctor’s order stating the purpose for the exam. The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM) and The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecology do not advocate the use of obstetric ultrasonography without a medical indication.
An ultrasound technician enjoys job security and a good salary. They can find employment in most places in the United States. CNBC.com reports the best states offering the best quality of life include New Hampshire, Vermont, Maine, and Minnesota. New Hampshire ranked first because of its excellent environment and a lower crime rate.
The average sonographer’s annual salary is $76,560, which is above the national average. Most ultrasound technicians work in hospitals and ambulatory care centers in metropolitan areas. The states that have most openings for medical sonographers include:
- California
- Texas
- Florida
- New York
- Pennsylvania
